Embark on a historical journey with our comprehensive APUSH Unit 6 practice test. This test will guide you through the pivotal events of the American Revolution, from its economic and political roots to its far-reaching impact. Get ready to test your knowledge and deepen your understanding of this transformative period.
In this practice test, you’ll explore the key concepts, major battles, and influential figures that shaped the American Revolution. Dive into the causes that sparked the conflict, the strategies employed by both sides, and the lasting legacy of this momentous event.
Overview of APUSH Unit 6
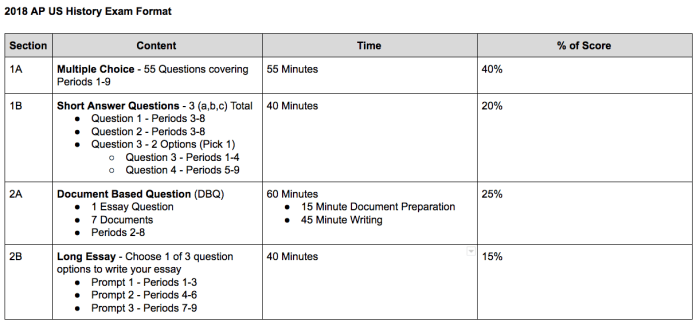
Unit 6 of APUSH, covering the period from 1877 to 1912, explores the transformative era of industrialization, urbanization, and social change in the United States. This unit examines the impact of these developments on American society, politics, and culture.
Key themes explored in Unit 6 include:
- The rise of industrial capitalism and the transformation of the American economy
- The growth of cities and the challenges of urbanization
- The emergence of new social movements and the struggle for social justice
- The expansion of American power and the rise of the United States as a global power
Some of the key events discussed in Unit 6 include:
- The Great Railroad Strike of 1877
- The rise of big business and the emergence of monopolies
- The growth of labor unions and the fight for workers’ rights
- The settlement of the American West and the impact on Native American tribes
- The Spanish-American War and the acquisition of overseas territories
Important historical figures featured in Unit 6 include:
- Andrew Carnegie, steel magnate and philanthropist
- John D. Rockefeller, founder of Standard Oil
- Samuel Gompers, labor union leader
- Theodore Roosevelt, president and advocate for conservation
- Woodrow Wilson, president and architect of the New Freedom
Causes of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was a complex event with multiple contributing factors. Economic, political, and social issues all played a role in the outbreak of hostilities between the American colonies and Great Britain.
Economic Factors
One of the most important economic factors that led to the Revolution was the British government’s policy of mercantilism. Mercantilism is an economic system in which the government regulates trade to benefit the mother country. In the case of the American colonies, this meant that the British government imposed a series of restrictions on colonial trade and industry.
These restrictions prevented the colonies from developing their own economies and led to widespread resentment among colonists.
Political Factors
In addition to economic factors, political factors also played a role in the American Revolution. The British government’s policies were often seen as arbitrary and unfair by colonists. For example, the British government imposed taxes on the colonies without giving them any representation in Parliament.
This led to the colonists feeling that they were being treated as second-class citizens.
Social Factors
Social factors also contributed to the American Revolution. The American colonies were a diverse society, with people from a variety of backgrounds and cultures. This diversity led to a number of social tensions, which were exacerbated by British policies. For example, the British government’s policy of favoring Anglicans over other religious groups led to resentment among non-Anglicans.
Enlightenment Ideas
The Enlightenment was a philosophical movement that emphasized reason and individualism. Enlightenment ideas had a profound impact on the American Revolution. American colonists were inspired by Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke, who argued that all people have natural rights to life, liberty, and property.
These ideas helped to shape the colonists’ view of themselves and their relationship to the British government.
Course of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was a bloody and protracted conflict that lasted for over seven years. Both sides employed a variety of strategies and tactics, and the outcome was often determined by the skill of the generals and the morale of the troops.
Major Battles and Campaigns, Apush unit 6 practice test
The American Revolution began with the Battles of Lexington and Concord in 1775. These battles were followed by a series of defeats for the Americans, including the Battle of Bunker Hill and the Battle of Long Island. However, the Americans won a major victory at the Battle of Saratoga in 1777, which convinced the French to enter the war on the side of the Americans.The
French alliance proved to be a major turning point in the war. The French provided the Americans with money, supplies, and troops. They also helped the Americans to blockade the British fleet and to capture the British army at Yorktown in 1781.
Strategies and Tactics
The British army was a professional force that was well-trained and well-equipped. The British used a variety of tactics to defeat the Americans, including frontal assaults, flanking maneuvers, and artillery barrages.The Americans were a ragtag army of farmers, merchants, and laborers.
They were not as well-trained or well-equipped as the British, but they were more familiar with the terrain and they were fighting for their homes. The Americans used a variety of tactics to defeat the British, including guerrilla warfare, hit-and-run attacks, and ambushes.
Role of Foreign Powers
The American Revolution was not just a conflict between the Americans and the British. Other countries, including France, Spain, and the Netherlands, also played a role in the war.France was the most important foreign power to aid the Americans. The French provided the Americans with money, supplies, and troops.
They also helped the Americans to blockade the British fleet and to capture the British army at Yorktown.Spain and the Netherlands also provided aid to the Americans, but their contributions were not as significant as those of France. Spain provided the Americans with money and supplies, while the Netherlands provided the Americans with loans and ships.The
aid provided by foreign powers was essential to the American victory. Without the help of France, Spain, and the Netherlands, the Americans would have likely lost the war.
Impact of the American Revolution
The American Revolution, a pivotal event in world history, had profound and far-reaching effects on American society, politics, and beyond. It marked a transformative period that shaped the development of the United States and influenced other nations worldwide.The revolution had both short-term and long-term consequences.
In the immediate aftermath, the colonies gained independence from British rule, establishing the United States of America. This newfound independence brought about significant political and social changes. The establishment of a republican form of government, based on the principles of popular sovereignty and limited government, marked a radical departure from the colonial era.
Long-Term Effects on American Society and Politics
The revolution’s long-term impact on American society and politics was equally profound. The Declaration of Independence, with its assertion of “unalienable Rights,” laid the foundation for a more egalitarian and democratic society. The revolution also accelerated the abolition of slavery, with the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 prohibiting slavery in new territories.The
revolution fostered a spirit of nationalism and unity among the American people. The shared experience of fighting for independence created a sense of common identity and purpose. This nationalism became a driving force in the expansion and development of the United States.
Influence on Other Countries
The American Revolution also had a profound impact on other countries around the world. It inspired revolutions in France, Latin America, and elsewhere, as people sought to emulate the ideals of liberty and self-determination. The revolution’s success demonstrated the possibility of overthrowing oppressive regimes and establishing independent nations.The
revolution also had a significant impact on the development of international law. The Treaty of Paris, which ended the war, established the principle of uti possidetis, which recognized the territorial boundaries of the newly independent United States. This principle became a cornerstone of international law, influencing the resolution of territorial disputes and the establishment of national boundaries.In
conclusion, the American Revolution had a transformative impact on American society, politics, and the world at large. Its legacy of liberty, democracy, and self-determination continues to inspire people around the globe. The revolution shaped the development of the United States, fostering a sense of national identity and unity, and played a pivotal role in the advancement of international law and the spread of democratic ideals.
APUSH Unit 6 practice test got you feeling a bit rusty? Why not take a break and delve into CNA Progression 2 Unit 7 ? It’s a great way to refresh your memory on healthcare basics. But don’t forget to come back and conquer that APUSH Unit 6 practice test like a pro!
Key Terms and Concepts
To fully understand APUSH Unit 6, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with key terms and concepts that define the era. This table provides a comprehensive list of these terms, along with their definitions and historical significance:
| Term | Definition | Historical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Coercive Acts | A series of laws passed by the British Parliament in response to the Boston Tea Party. | These acts aimed to punish Massachusetts and assert British authority, escalating tensions between the colonies and Great Britain. |
| Continental Army | The military force established by the Continental Congress to fight for American independence. | Under the leadership of George Washington, the Continental Army played a pivotal role in securing victory in the Revolutionary War. |
| Declaration of Independence | A document drafted by Thomas Jefferson that proclaimed the American colonies’ independence from British rule. | Adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, the Declaration of Independence marked a decisive moment in the American Revolution. |
| Loyalists | Individuals who remained loyal to the British Crown during the American Revolution. | Loyalists, also known as Tories, faced persecution and property confiscation by Patriots. |
| Mercantilism | An economic system in which the colonies were expected to provide raw materials for the mother country and purchase finished goods in return. | Mercantilism led to resentment among the colonists, who felt exploited by British trade policies. |
| Patriots | Individuals who supported American independence from British rule. | Patriots, also known as Whigs, played a crucial role in organizing resistance to British policies and advocating for independence. |
| Proclamation of 1763 | A British law that prohibited settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains. | The Proclamation of 1763 aimed to appease Native American tribes and prevent conflicts with colonists. |
| Stamp Act | A British tax on printed materials, such as newspapers and legal documents. | The Stamp Act sparked widespread protests and resistance in the colonies, contributing to the growing tensions between Britain and America. |
| Townshend Acts | A series of British laws that imposed duties on imported goods. | The Townshend Acts further inflamed colonial resentment and led to boycotts and protests. |
Understanding these key terms and concepts will enhance your comprehension of the events, causes, and consequences of the American Revolution.
Practice Questions
To evaluate students’ comprehension of APUSH Unit 6, a comprehensive set of practice questions has been devised. These questions encompass a variety of formats, including multiple choice, short answer, and essay questions, catering to diverse learning styles and assessing different levels of understanding.
Answer keys or grading rubrics accompany each question, providing students with clear guidance on the expected responses and facilitating effective self-assessment.
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions test students’ ability to identify the correct answer from a set of options. These questions cover key concepts, events, and figures from APUSH Unit 6.
- Which of the following was a major cause of the American Revolution?
- British mercantilist policies
- French and Indian War
- Enlightenment ideas
- All of the above
- Who was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence?
- Thomas Jefferson
- John Adams
- Benjamin Franklin
- George Washington
Answer:d. All of the above
Answer:a. Thomas Jefferson
Short Answer Questions
Short answer questions require students to provide concise and specific answers to questions related to APUSH Unit 6.
- Explain the significance of the Boston Tea Party.
- Describe the major battles of the American Revolution.
Answer:The Boston Tea Party was a protest against British taxation and a catalyst for the American Revolution.
Answer:Major battles of the American Revolution include the Battle of Saratoga, the Battle of Yorktown, and the Battle of Trenton.
Essay Questions
Essay questions assess students’ ability to synthesize information, develop arguments, and write effectively about APUSH Unit 6.
- Analyze the causes of the American Revolution. Explain how different factors contributed to the growing tensions between the British government and the American colonists.
- Discuss the impact of the American Revolution on the United States. Consider the political, social, and economic changes that resulted from the war.
FAQ: Apush Unit 6 Practice Test
What is the purpose of this practice test?
To help students assess their understanding of APUSH Unit 6 and prepare for the APUSH exam.
What topics are covered in this practice test?
The practice test covers the key concepts, events, and figures related to the American Revolution, as Artikeld in APUSH Unit 6.
What types of questions are included in this practice test?
The practice test includes a variety of question types, such as multiple choice, short answer, and essay questions.