Match the heavy metal product with its antimicrobial use sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of heavy metal products and their remarkable antimicrobial properties, providing a thorough examination of their mechanisms of action, antimicrobial spectrum, and factors influencing their efficacy. By exploring the potential for resistance and the diverse applications of these products in various settings, this discourse unravels the intricate relationship between heavy metals and their role in combating microbial threats.
1. Heavy Metal Products and Their Antimicrobial Uses
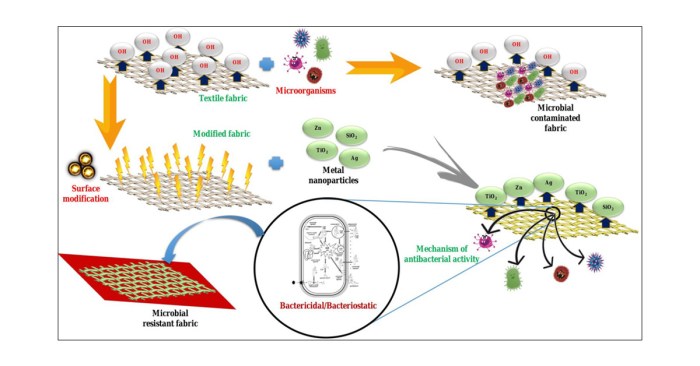
Heavy metal products have been extensively used for antimicrobial purposes due to their ability to inhibit the growth and proliferation of microorganisms. These products include silver, copper, zinc, mercury, and bismuth, each with distinct mechanisms of action.
Silver
Silver ions are highly effective against a wide range of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. They disrupt microbial cell membranes, leading to leakage of cellular contents and inhibition of essential metabolic processes.
Copper
Copper ions have antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. They bind to proteins and enzymes, disrupting their function and inhibiting microbial growth.
Zinc
Zinc ions are essential for microbial growth, but at high concentrations, they become toxic. Zinc ions inhibit the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids, leading to cell death.
Mercury
Mercury compounds are highly toxic to microorganisms. They bind to proteins and enzymes, disrupting their function and causing cell damage.
Bismuth, Match the heavy metal product with its antimicrobial use
Bismuth compounds have antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. They form complexes with proteins and enzymes, inhibiting their function and disrupting microbial metabolism.
2. Antimicrobial Spectrum of Heavy Metal Products: Match The Heavy Metal Product With Its Antimicrobial Use
Heavy metal products have a broad antimicrobial spectrum, targeting a wide range of microorganisms. They are effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even some protozoa.
Bacteria
Heavy metal products are particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureusand Streptococcus pneumoniae. They also have some activity against Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coliand Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Viruses
Silver and copper ions have been shown to have antiviral activity against viruses such as influenza, herpes simplex virus, and HIV.
Fungi
Heavy metal products are effective against a variety of fungi, including Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Cryptococcus neoformans.
Protozoa
Some heavy metal products, such as bismuth, have been shown to have antiprotozoal activity against Giardia lambliaand Entamoeba histolytica.
3. Factors Influencing Antimicrobial Activity
The antimicrobial activity of heavy metal products is influenced by several factors, including concentration, contact time, and environmental conditions.
Concentration
The higher the concentration of heavy metal ions, the greater the antimicrobial activity. However, high concentrations of heavy metal ions can also be toxic to human cells.
Contact Time
The longer the contact time between heavy metal ions and microorganisms, the greater the antimicrobial activity. This is because it allows more time for the ions to penetrate microbial cells and disrupt their metabolism.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions, such as pH and temperature, can affect the antimicrobial activity of heavy metal products. For example, silver ions are more effective in acidic environments, while copper ions are more effective in neutral or alkaline environments.
FAQ Insights
What are the most common heavy metal products used for antimicrobial purposes?
Silver, copper, zinc, and mercury are among the most widely used heavy metal products for antimicrobial applications.
How do heavy metal products exert their antimicrobial effects?
Heavy metal products can disrupt microbial cell membranes, interfere with enzyme function, and generate reactive oxygen species, leading to microbial cell death.
What factors can influence the antimicrobial activity of heavy metal products?
Factors such as concentration, contact time, temperature, pH, and the presence of organic matter can affect the antimicrobial efficacy of heavy metal products.
Is there a potential for microorganisms to develop resistance to heavy metal products?
Yes, microorganisms can develop resistance to heavy metal products through various mechanisms, such as efflux pumps, reduced uptake, and enzymatic detoxification.