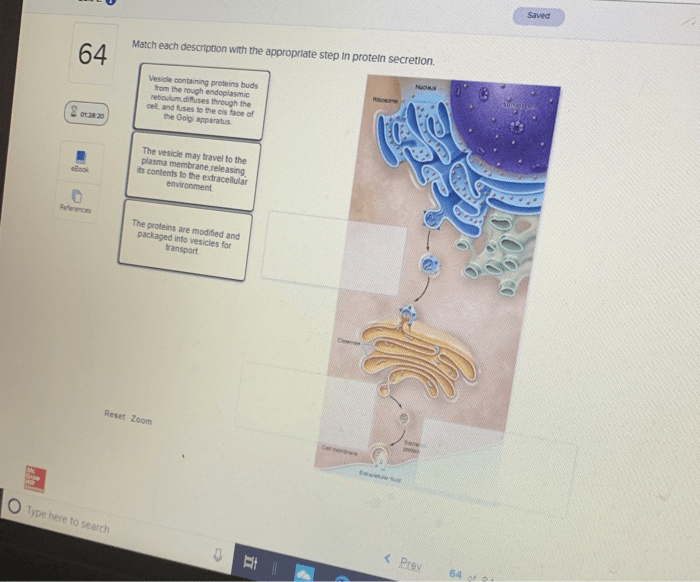
Match each description with the appropriate step in protein secretion. Protein secretion is a complex process that involves multiple steps, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding these steps is essential for comprehending how proteins are produced and transported within the cell.
The first step in protein secretion is protein synthesis and folding. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, while the process of protein folding is influenced by factors such as amino acid sequence, chaperones, and the environment. Once a protein is folded, it is ready to be transported to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Protein Secretion
Protein secretion is a vital cellular process that enables cells to release newly synthesized proteins into the extracellular environment. This process involves a series of intricate steps that ensure the correct folding, modification, and targeting of proteins to their designated destinations.
Protein Synthesis and Folding
Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. The mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm, where it is translated into a polypeptide chain by ribosomes. As the polypeptide chain emerges from the ribosome, it begins to fold into its native conformation.
The correct folding of proteins is essential for their function and is influenced by factors such as amino acid sequence, chaperone proteins, and the cellular environment.
ER Translocation and Glycosylation
Once the polypeptide chain is synthesized, it is translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The ER is responsible for protein folding, disulfide bond formation, and glycosylation. Glycosylation is the attachment of sugar molecules to proteins and can affect their stability, solubility, and function.
Golgi Apparatus Processing and Sorting
From the ER, proteins are transported to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus is a complex of flattened membranous sacs that modify and sort proteins. Proteins can undergo further glycosylation, phosphorylation, and other modifications in the Golgi apparatus. Additionally, the Golgi apparatus plays a crucial role in sorting proteins to their final destinations, such as the plasma membrane, lysosomes, or secretory vesicles.
Vesicle Formation and Transport, Match each description with the appropriate step in protein secretion
Once proteins are processed and sorted in the Golgi apparatus, they are packaged into transport vesicles. These vesicles bud from the Golgi apparatus and travel along microtubules to their target destinations. The vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents into the extracellular environment, or they can fuse with other organelles, such as lysosomes.
Protein Secretion
The final step of protein secretion is exocytosis, where the contents of the secretory vesicles are released into the extracellular environment. Exocytosis is a regulated process that is controlled by various cellular signals. The secreted proteins can perform a wide range of functions, including cell-cell communication, immune response, and tissue repair.
Frequently Asked Questions: Match Each Description With The Appropriate Step In Protein Secretion
What is the role of ribosomes in protein secretion?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, which is the first step in protein secretion.
What is protein folding?
Protein folding is the process by which a protein assumes its native conformation. This process is influenced by factors such as amino acid sequence, chaperones, and the environment.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in protein secretion?
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing and sorting proteins. It modifies proteins and sorts them into vesicles for transport to different cellular compartments.