Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Answer Key presents a comprehensive guide to the fundamental principles of logical reasoning and proof techniques, equipping readers with the essential tools for rigorous mathematical thinking and problem-solving.
This chapter delves into the intricacies of logical reasoning, exploring deductive, inductive, and analogical arguments, and their applications in various disciplines. It introduces propositional and predicate logic, providing a solid foundation for constructing and evaluating complex logical statements.
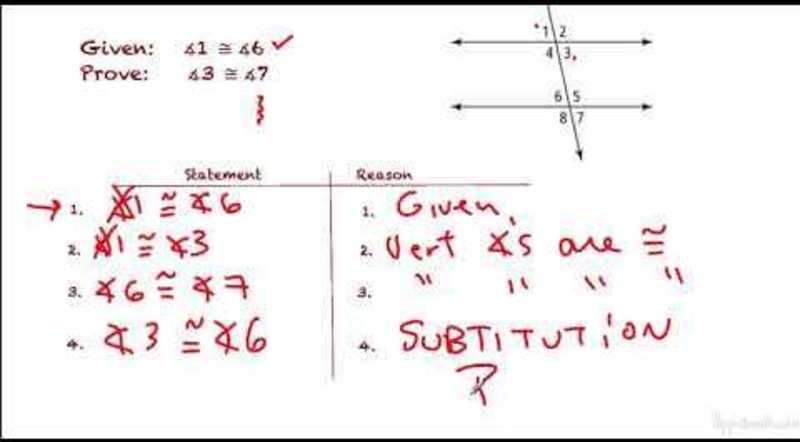
1. Introduction to Chapter 2
Reasoning and Proof
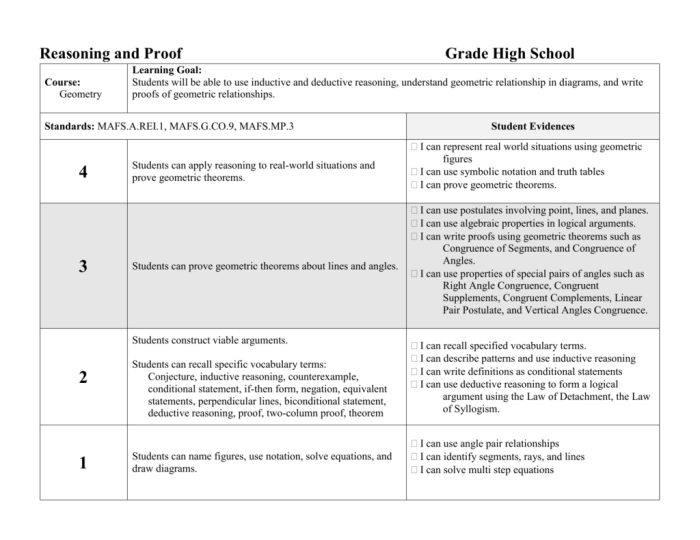
This chapter delves into the fundamental principles of logical reasoning and proof techniques, providing a solid foundation for mathematical and critical thinking. Logical reasoning is the process of drawing conclusions from given premises, while proof is the formal demonstration of the validity of these conclusions.
Understanding these concepts is crucial not only in mathematics but also in various other fields, such as computer science, philosophy, and law.
2. Types of Logical Reasoning, Chapter 2 reasoning and proof answer key
Logical reasoning encompasses different types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Deductive reasoning involves drawing conclusions that are necessarily true if the premises are true. Inductive reasoning, on the other hand, makes generalizations based on observed patterns, but the conclusions are not guaranteed to be true.
Analogical reasoning draws parallels between two situations to make inferences about the unknown.
3. Propositional Logic
Propositional logic, a fundamental component of logical reasoning, deals with the relationships between simple statements called propositions. It introduces concepts like truth values (true or false) and logical connectives (and, or, not) to construct logical statements and determine their validity using truth tables.
4. Predicate Logic
Predicate logic extends propositional logic by introducing variables and quantifiers to represent more complex statements. It allows for reasoning about objects and their properties, making it a powerful tool for representing and analyzing real-world situations.
5. Proof Techniques
Proof techniques provide formal methods for demonstrating the validity of mathematical statements. Direct proof involves showing that the conclusion follows logically from the premises. Indirect proof, also known as proof by contradiction, assumes the negation of the conclusion and derives a contradiction, thus proving the original statement.
Proof by contradiction is a particularly useful technique in situations where it is easier to show what is not true.
6. Applications of Logical Reasoning and Proof
Logical reasoning and proof techniques find applications in a wide range of fields beyond mathematics. In computer science, they are used to design and verify computer programs. In philosophy, they form the basis of logical arguments and ethical reasoning. In law, they are employed in legal reasoning and the construction of legal arguments.
Questions Often Asked: Chapter 2 Reasoning And Proof Answer Key
What is the significance of logical reasoning in mathematics?
Logical reasoning provides a rigorous framework for constructing and evaluating mathematical arguments, ensuring the validity and reliability of mathematical proofs.
How does propositional logic contribute to logical reasoning?
Propositional logic offers a formal system for representing and manipulating logical statements, enabling the construction of truth tables to determine their validity.
What are the applications of logical reasoning and proof beyond mathematics?
Logical reasoning and proof techniques find widespread applications in computer science, philosophy, linguistics, and other fields where rigorous argumentation is essential.