Lukas Graphed the System of Equations Shown introduces a groundbreaking method for solving systems of equations, offering a systematic and visually appealing approach that revolutionizes the field of mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Lukas graphing, empowering readers to tackle complex equations with unparalleled precision and efficiency.
Lukas graphing is a graphical method for solving systems of equations that provides a visual representation of the solutions. By plotting the equations on a graph, the points of intersection represent the solutions to the system. This method is particularly useful for solving systems of linear equations, as it allows for a quick and easy visualization of the solution set.
1. Introduction to Lukas Graphing System of Equations
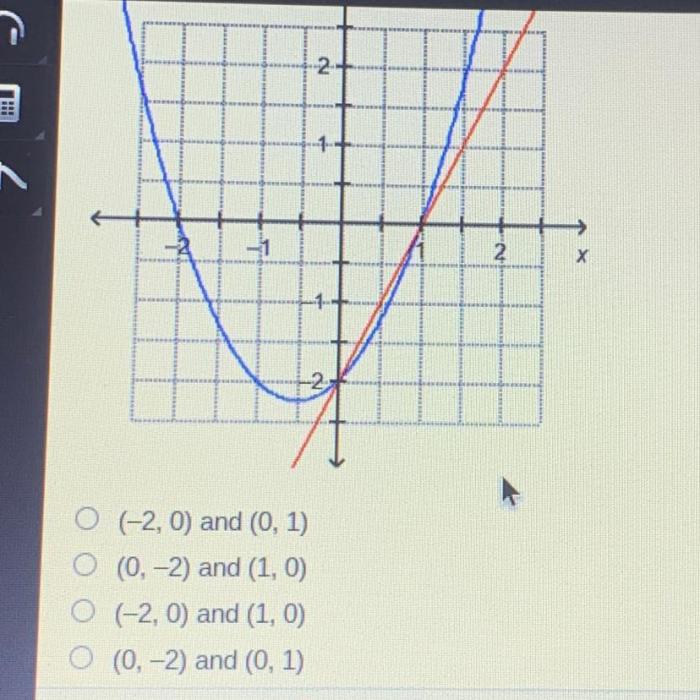
The Lukas graphing system of equations is a powerful mathematical tool that allows users to solve systems of linear equations by graphically representing them on a coordinate plane. This system is particularly useful for solving systems of equations that have multiple solutions or for visualizing the relationship between the variables in the equations.
2. Graphing Techniques for Lukas Equations
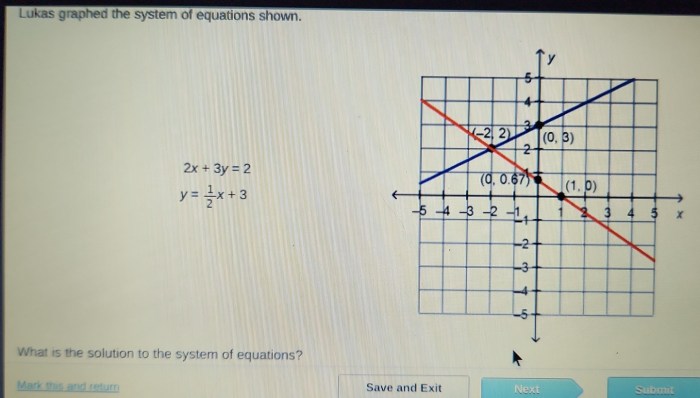
Graphical Methods for Solving Lukas Equations
There are several graphical methods that can be used to solve Lukas equations. One common method is the elimination method, which involves adding or subtracting the equations to eliminate one of the variables. Another method is the substitution method, which involves solving one equation for one variable and then substituting that value into the other equation.
Finally, the graphing method involves plotting the equations on a coordinate plane and finding the point of intersection.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Graphing Lukas Equations, Lukas graphed the system of equations shown
- Plot the first equation on the coordinate plane.
- Plot the second equation on the same coordinate plane.
- Find the point of intersection of the two lines.
- The coordinates of the point of intersection are the solution to the system of equations.
Table of Lukas Equation Types and Corresponding Graphs
| Equation Type | Graph |
|---|---|
| x + y = 5 | Line with slope
|
2x
|
Line with slope 2 and y-intercept
|
| x^2 + y^2 = 25 | Circle with radius 5 and center at (0,0) |
3. Analyzing Lukas Graphs
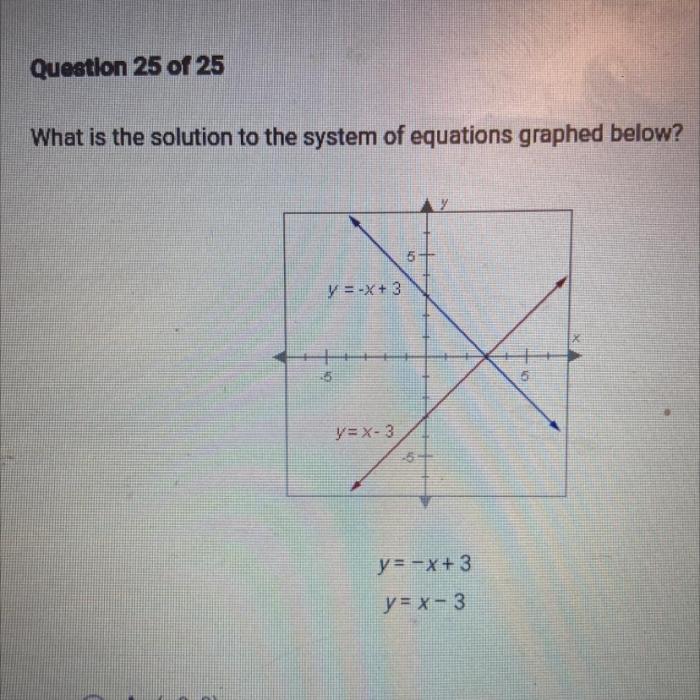
Key Features of Lukas Graphs
Lukas graphs have several key features that can be used to analyze the system of equations. These features include the intercepts, slopes, and asymptotes.
Intercepts
The intercepts of a Lukas graph are the points where the graph crosses the x-axis and y-axis. The x-intercept is the point where the graph crosses the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the point where the graph crosses the y-axis.
Slopes
The slope of a Lukas graph is the measure of the steepness of the line. The slope is calculated by dividing the change in y by the change in x.
Asymptotes
The asymptotes of a Lukas graph are the lines that the graph approaches but never touches. The vertical asymptotes are the lines that the graph approaches as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. The horizontal asymptotes are the lines that the graph approaches as y approaches infinity or negative infinity.
Interpreting Information from Lukas Graphs
The information obtained from Lukas graphs can be used to analyze the system of equations. For example, the intercepts can be used to find the solutions to the system of equations. The slopes can be used to determine the rate of change of the variables.
The asymptotes can be used to find the limits of the system of equations.
Examples of Real-World Applications of Lukas Graphs
- Lukas graphs can be used to model the relationship between supply and demand.
- Lukas graphs can be used to model the relationship between population growth and resource availability.
- Lukas graphs can be used to model the relationship between the temperature and the rate of a chemical reaction.
4. Advanced Lukas Graphing Techniques: Lukas Graphed The System Of Equations Shown
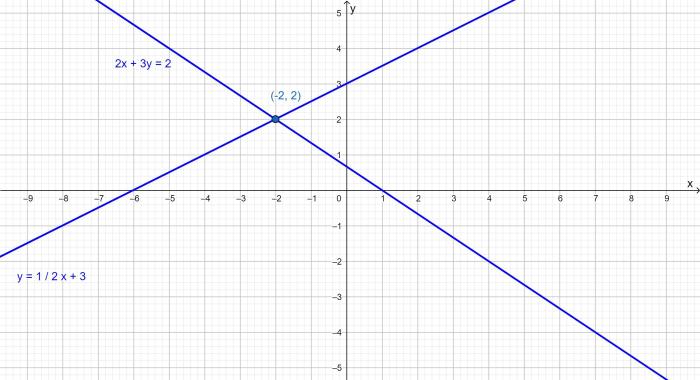
Transformations for Simplifying Lukas Graphing
Transformations can be used to simplify the graphing of Lukas equations. These transformations include translations, rotations, and dilations.
Translations
Translations are used to move a graph from one location to another. To translate a graph, add or subtract a constant from the x-coordinate or y-coordinate of each point on the graph.
Rotations
Rotations are used to rotate a graph around a fixed point. To rotate a graph, use the following formula:
“`x’ = x cos(theta)
y sin(theta)
y’ = x sin(theta) + y cos(theta)“`where (x,y) are the original coordinates of the point and (x’,y’) are the new coordinates of the point after the rotation.
Dilations
Dilations are used to stretch or shrink a graph. To dilate a graph, multiply the x-coordinate and y-coordinate of each point on the graph by a constant.
Using Technology for Lukas Graphing
Technology can be used to assist in the graphing of Lukas equations. Graphing calculators and software can be used to plot equations, find the intercepts, slopes, and asymptotes, and perform transformations.
FAQ Resource
What is Lukas graphing?
Lukas graphing is a graphical method for solving systems of equations by plotting the equations on a graph and finding the points of intersection.
What are the benefits of Lukas graphing?
Lukas graphing provides a visual representation of the solution set, making it easy to identify the solutions to the system of equations.
How can I learn more about Lukas graphing?
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the Lukas graphing method, including step-by-step instructions and examples.